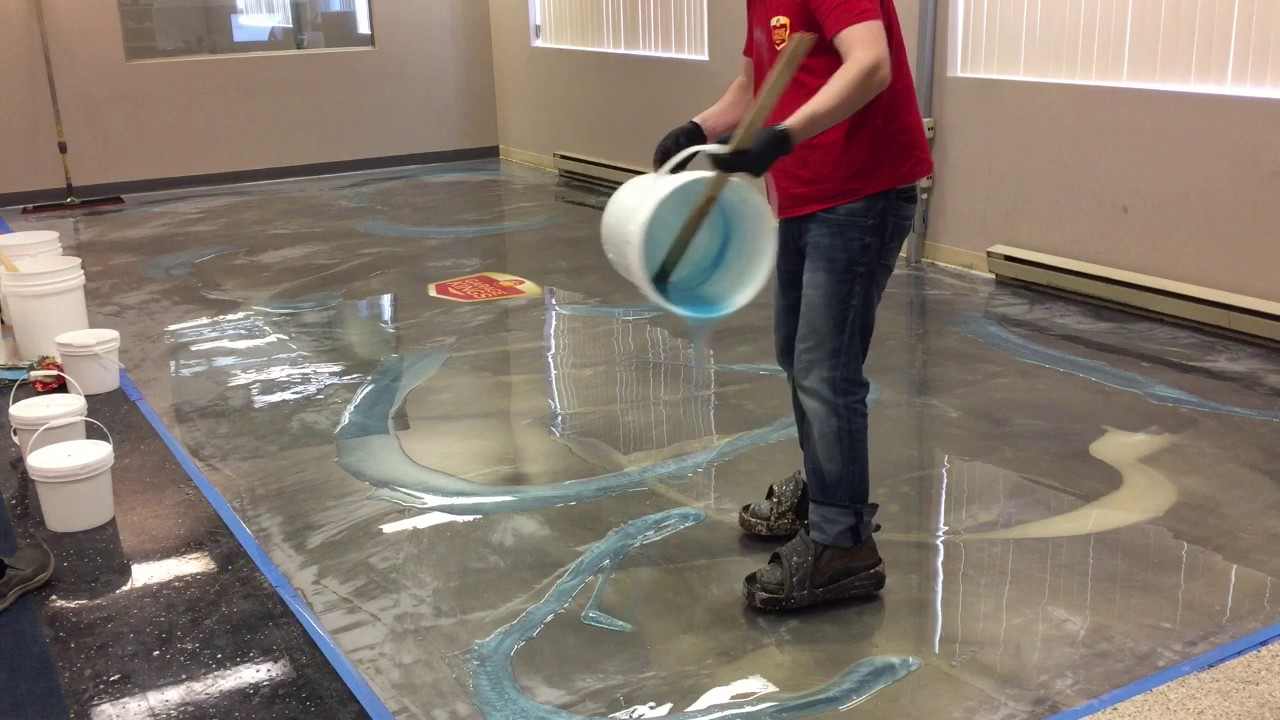
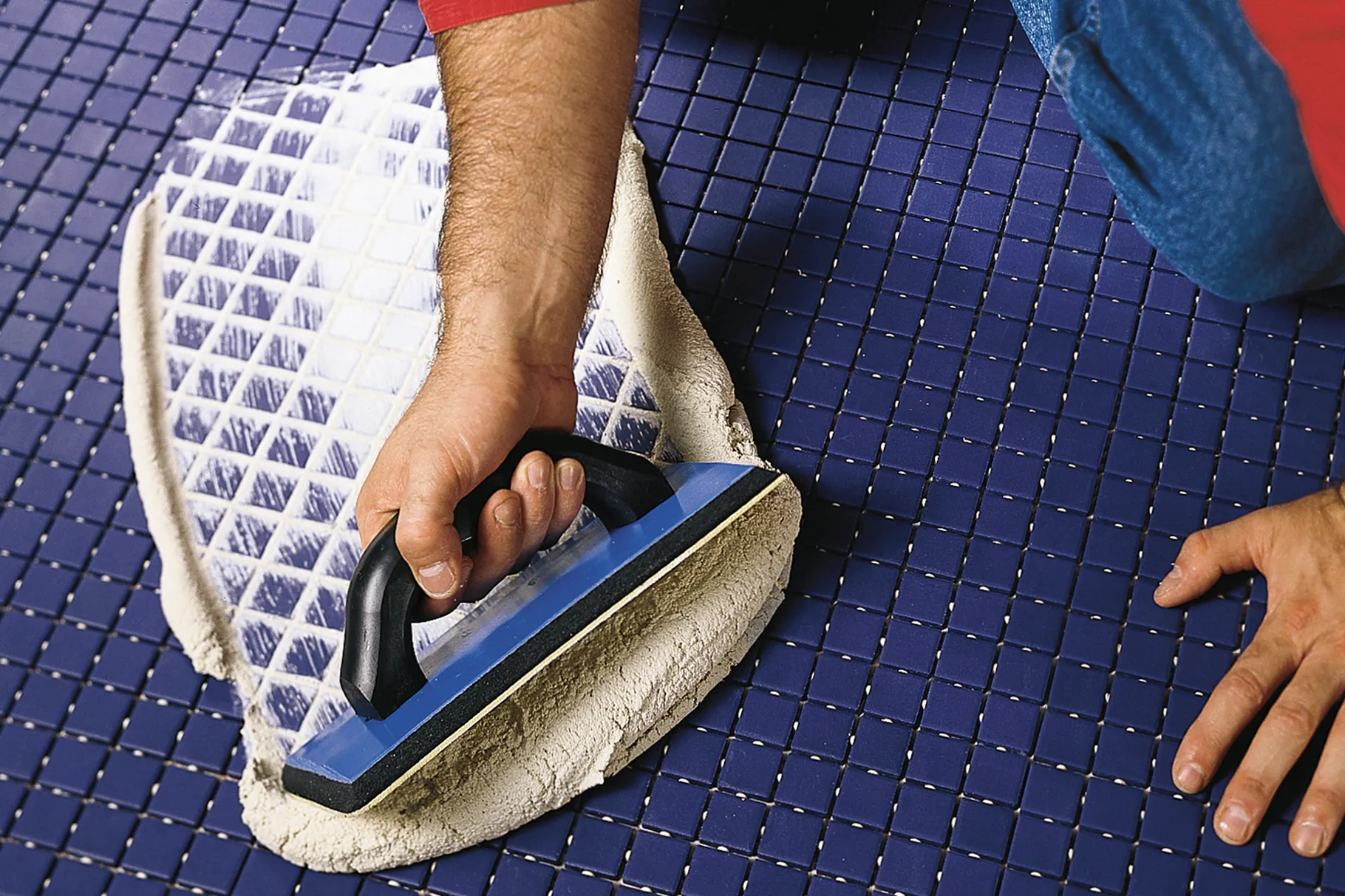
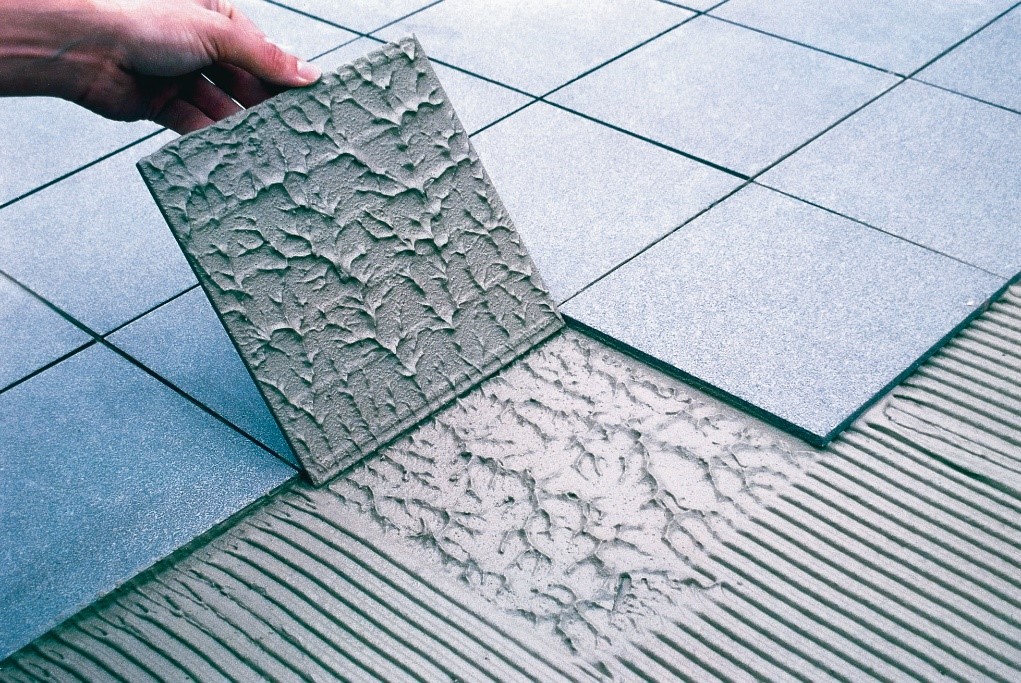
Grouting in construction is the technique of filling gaps, spaces, or seams between two materials, such as stones, tiles, marbles, and so on. There are many types of tile grouts. Choosing the right grout is an essential step in every tiling project. With a variety of options available, such as Cement Grout, Advanced Performance Grout, Epoxy Grouting, and Premixed Grout – it is important to know which product is right for your job.
Purpose of grouting
- Grout remains a viscous compound made up of cement, water, sand, epoxy, acrylic, and polymer that finds use as a filler between ceramic and stone tiles.
- It repairs concrete fractures, fills tile gaps, and waterproofs surfaces.
- It is done to provide the foundation of a load-bearing structure with more strength.
- Also, it alters the structure’s physical qualities.
- The process limits seepage and prevents landslides.
- Surface subsidence can be reduced by grouting.
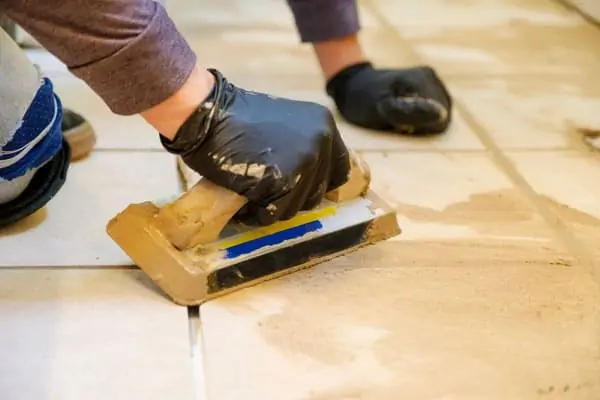

Image Source: Constrofacilitator
Types of tile grout
We use tiling grout to fill spaces between tiles. Also, it aids in the securement of the tile to its base and functions as a sealant to keep moisture out of joints:
Cement-based non-sanded grout remains suitable for use on tile surfaces. It remains dry when you place the grout. Also, it commonly finds use in smaller tile joints.
Sanded grout, which is a cement-based mortar with minute sand grains added to aid the setting and give a stronger grout, is commonly used in larger joints. It should first be tested to ensure that the sand does not scratch the tile.
Epoxy grouting material is water-resistant and doesn’t need to be sealed after installation. It also inhibits the growth of microorganisms and minimizes cracking. When tiles are exposed to a lot of water, chemicals, or oil, this sort of grout is perfect. It comes in both sanded and unsanded forms.
Watch this video to learn about different grout products, applications, and advantages.