Efficient HVAC systems make buildings safer and healthier. These systems may use fresh air from external surroundings to regulate temperature and humidity. All HVAC types use several components such as the thermostat, heating unit, etc. for air conditioning.
Specially-trained HVAC consultants are an important authority in the industry because HVAC & its types are an integral part of a building. No building is now complete without a proper HVAC system.
Given its crucial role in determining the temperature and quality of air, it becomes all the more important to know its basics. This way, you can not only avoid faulty installation but also prevent any future shortcomings. Moreover, you will also avoid any premature wear and tear or an expensive breakdown of the HVAC types & their units.
Contents
- 1 What are HVAC systems?
- 2 Need for HVAC Systems in Buildings
- 3 Heating in HVAC systems
- 4 Ventilation in HVAC systems
- 5 Air Conditioning in HVAC systems
- 6 Types of HVAC systems
- 7 Components of HVAC Systems
- 8
- 9 Energy-efficient HVAC Systems
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 Best AC brand in India | Top 10 air conditioners with prices
What are HVAC systems?
The HVAC full form is Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning with respect to building structures. HVAC systems & types are important areas in the field of mechanical engineering.
Basically, HVAC means the various systems and types used for moving air between different indoor and outdoor spaces. In addition to that, HVAC also offers heating and cooling in both residential and commercial buildings.
HVAC systems ensure the air quality of a building. From residential buildings like houses and apartments to commercial buildings like offices and hospitals, all use an HVAC system.
Need for HVAC Systems in Buildings
An HVAC system is a necessity, not a choice. Why is it a must-have requirement for all residential, commercial, and industrial buildings? HVAC systems play a crucial role in the maintenance of indoor air quality.
In research by Environmental Protection Agency, poor air quality was the largest factor for environment-related sickness. Efficient HVAC systems solve this problem. It circulates the air, regulates the temperature according to the weather, and removes harmful particles or gases from the air.
These features greatly reduce the risk of allergies, lung-related problems, and seasonal flu.
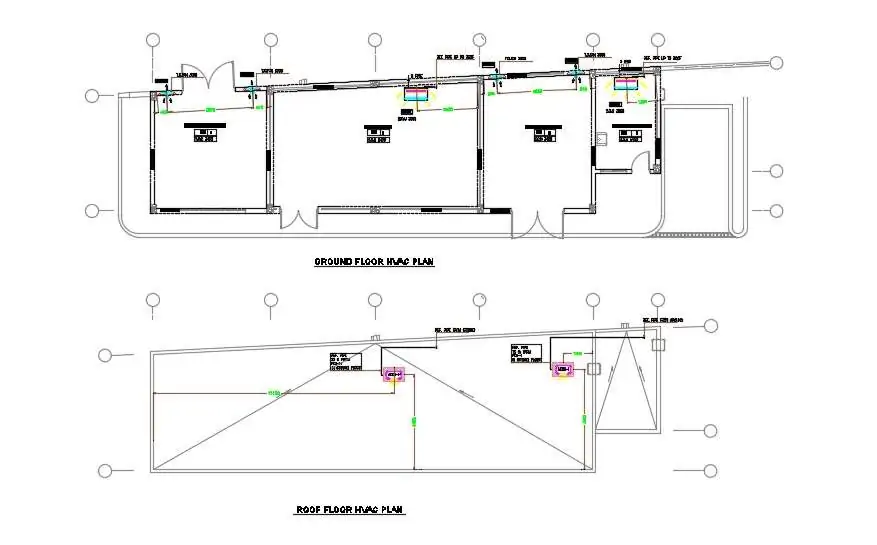
Image Source: cadbull.com
| Also see: Air conditioning system – Everything you need to know about! |
Heating in HVAC systems
Most people are aware of the concept of heaters as heating units. Who doesn’t warm up their room during the winters with a convector heater?
Now, imagine a system that centrally heats an entire building. That is what the heating aspect of HVAC systems is about. A heating unit like a boiler or a heat pump heats water or air in a furnace or a large mechanical room. The process of conduction or convection transfers heat from this heating unit of the HVAC systems to all the areas of the building.
Pipes transport heat created by water or steam in the heating unit to other areas. A circulator or a heat pump in the heating unit moves the hot water to distribution systems. Wall-mounted or floor-installed radiators transfer heat throughout the building. The transfer of heat using steam or water is known as Hydronics.
The heat from the air is transferred through ducts that are heat-resistant. In this system, the air needs to be filtered for dust and other particles.
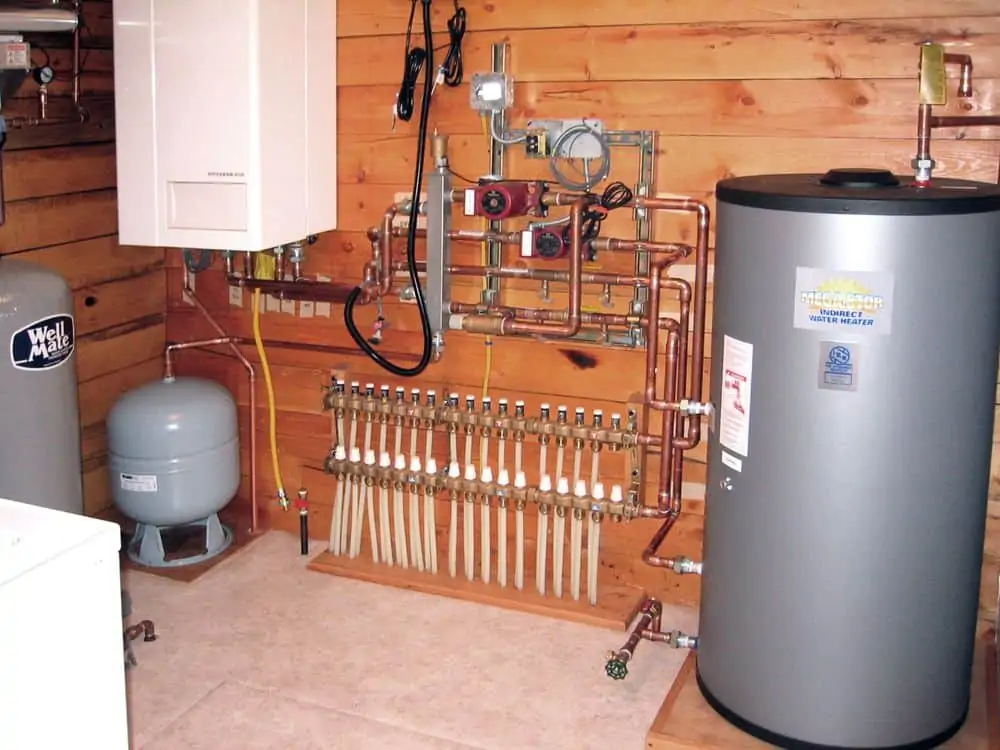

Image Source: pinterest.com
Generally, a commercial building that has a large number of people does not need a lot of heat production. The balance should be maintained for the building to feel pleasantly warm.
| Also see: Shop for the right room heater online at best price with these tips! |
Ventilation in HVAC systems
The indoor air quality of a building has a direct correlation to the health of the people who reside or work in that building.
The process of ventilation ensures the exchange of air in any space. It replaces the stale air from the inside with the fresh air from the outside.
Ventilating space includes temperature control and the replenishment of oxygen. It removes odors, smoke, carbon dioxide, moisture, dust, and bacteria from a building.
Ventilation is an intentional procedure. It is either natural or mechanical. Natural modes of ventilation are concerned with open windows and any such source of airflow. Mechanical ventilation, on the other hand, specifically directs fresh air via ducts and vents.
| Click here for an automatic ventilation solution. |
Air Conditioning in HVAC systems
A standalone air conditioner is a part of most urban homes now. It provides cooling and humidity control for one room. In the same manner, a central air conditioning system cools a commercial building and regulates humidity inside it.
Office buildings with heavy-duty computer systems need cooling to prevent over-heating. Sealed windows help in keeping the air cool for longer periods of time.
Vents draw fresh air from the outside and route it to a mixed air chamber. From this chamber, the mixed air goes into a heat exchanger. The air cools down and makes its way into space it is meant to be cooling.
Heat removal through convection and conduction provides air conditioning. Power consumption is high in order to cool a large area. Hence, air conditioning systems should have sufficient horsepower.
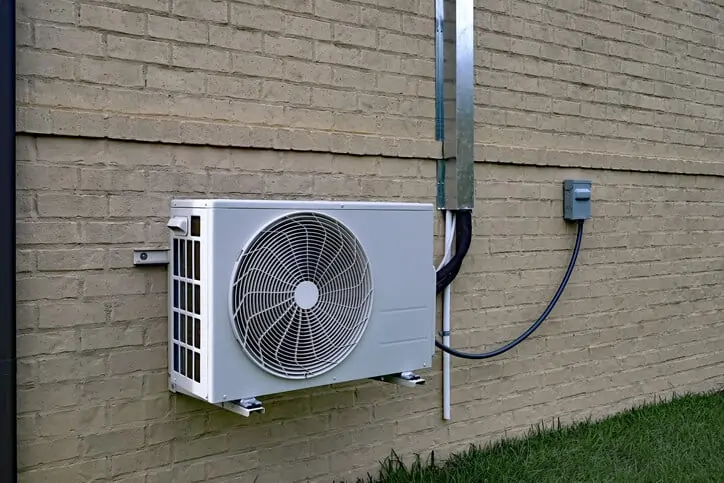

Image source: modernize.com
Types of HVAC systems
Choosing the right type of HVAC system is important. There are three main types of HVAC systems used in commercial buildings: Split HVAC Systems, VRF or VRV systems and, CAV and VAV systems.
Split HVAC Systems
As the name suggests, the split HVAC systems consist of two different units- an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. An air handler (indoor unit), a condenser (outdoor unit), a thermostat, an air filter, and ducts are the components of such a system.
Split HVAC systems are further classified into single-split and multi-split systems.
Single-Split HVAC Systems
It is a compact system that is suitable for small commercial spaces. The installation procedure is quite simple. This system is affordable.
Cafes, shops, and offices usually opt for this HVAC system.
Multi-Split HVAC Systems
It is a more expansive system. Multiple indoor units are connected to one outdoor unit. The installation requires professional help.
This system finds use in larger spaces like clinics and restaurants.
VRV or VRF HVAC systems
VRV (Variable Refrigerant Volume) or VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) uses a refrigerant for heating and cooling. This system uses just one condenser for more than one evaporator. Thus, this system is perfect for medium and large commercial buildings.
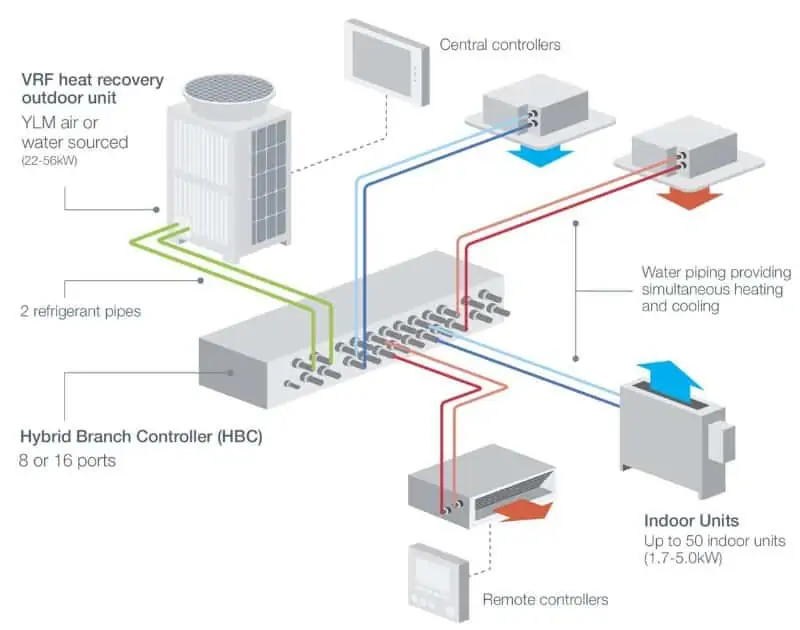
Image source: arialtd.co.uk
VRV systems are of two types:
Heat Pump Systems- heating unit
They can provide either coolness or heat at one time.
Heat Recovery Systems- heating unit
They can provide coolness and heat at the same time.
CAV and VAV HVAC Systems
The CAV (Constant Air Volume) system is best for manufacturing factories where the temperature is stable for long periods of time. The compressor operates at full capacity in order to reach the ideal temperature.
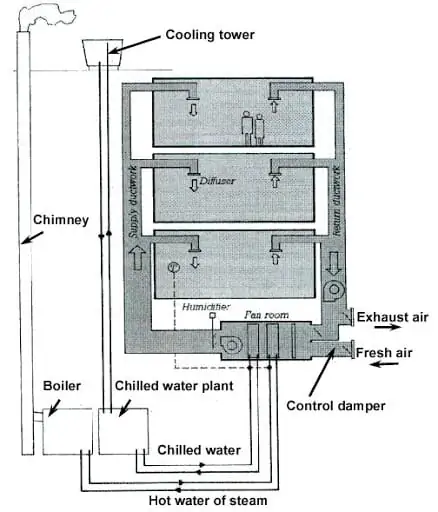
Image source: pages.drexel.edu
The VAV (Variable Air Volume) system is more energy-efficient than the CAV system. Buildings that require a range of heating and cooling use the VAV system. The speed of the compressor depends on the temperature needed.
Components of HVAC Systems
The HVAC systems comprise several components. They work together to adjust the temperature and ensure fresh air in the building.
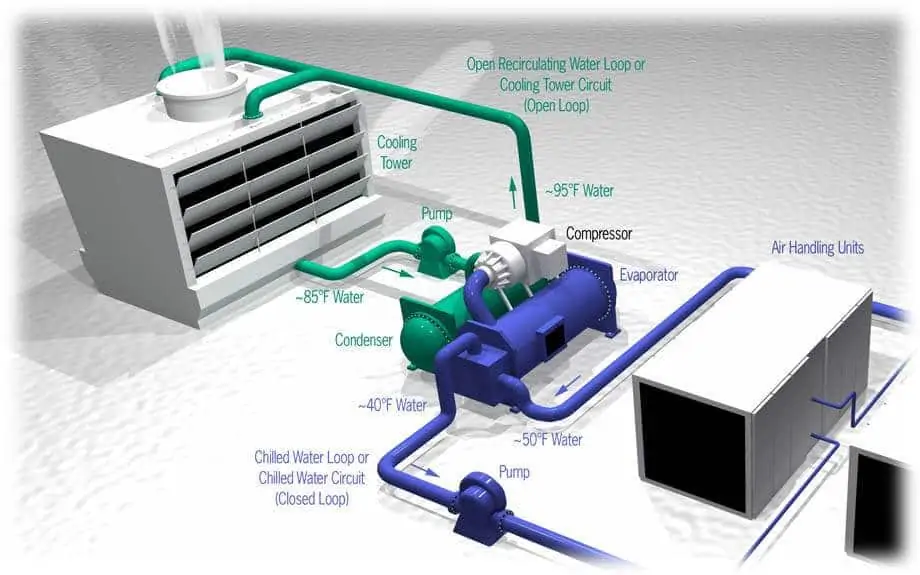
Image source: instrumentationtools.com
The main components of the commercial HVAC systems are:
Air Handler or Blower Units
These units usually comprise of:
-
Condensate system: Warm moist air, after cooling, produces water (condensate). The condensate runs down the evaporator coil into a pan. This pan drains the water through the pipes to dispose of it.
-
Condensate pump: It’s a small pump that collects and pumps water to a drain. Condensate pumps come into the picture when a building can’t rely on gravity for disposal.
-
Condensate Overflow Pan: It is a safety device that prevents leaks and spills. Condensate Overflow Pan either has a separate drain or a float switch that can shut down the AC if the pan is full.
-
Blower Fan: It circulates the air inside the building. Air is moved at different speeds when the heating and cooling functions are simultaneous.
-
Electrical Controls: These consist of the shut-down switch as well as the fuse that protects an AC circuit from overheating.
Evaporator Coil (Cooling Coil)
High-pressure refrigerant liquid, released into the cooling coil by the thermal expansion valve changes state from a liquid to a gas, causing a drop in temperature of the refrigerant and thus cooling the evaporator coil so that when we move air across the coil the air will, in turn, be cooled.
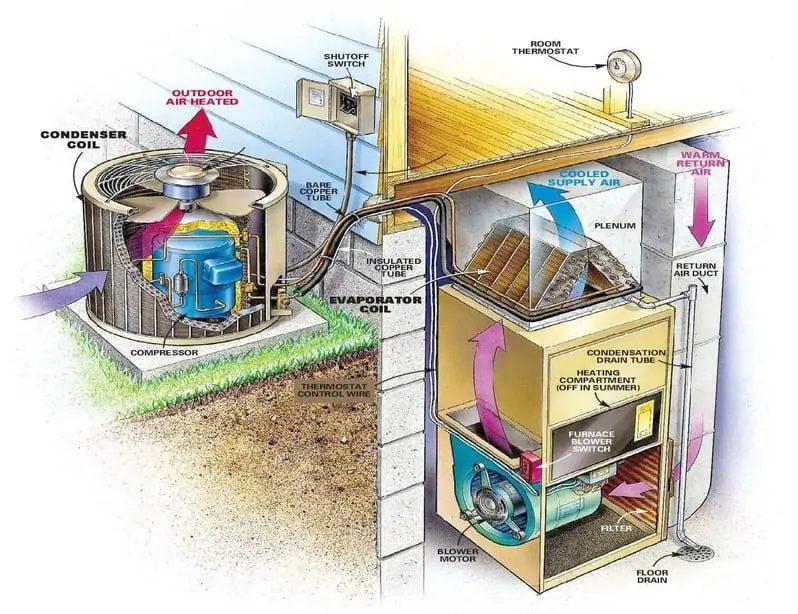
Image source: energy-starservices.com
-
Return Plenum: The return plenum is connected to the return duct system. It is a compartment that receives air and provides it to the blower fan.
-
Supply plenum: Supply plenum is connected to the supply duct system. It is a compartment that collects air. The return plenum and supply plenum are like “junction boxes” to which return ducts or supply ducts respectively can be connected.
-
Support system: It is the means by which an attic-mounted air handler is supported or held in place. You may suspend it from the roof rafters or place it on supporting wood beams.
Thermal Expansion Valve
An air conditioner thermal expansion valve is a device located at the cooling coil and connected between the incoming refrigerant line and the refrigerant inlet to the cooling coil in the air handler.
The air conditioning system thermal expansion valve or “TEV” is a device that regulates the flow of refrigerant from the incoming high-pressure side (from the compressor/condenser) into the low-pressure side (in the cooling coil).
Ducts and Vents for HVAC systems

Image source: rinaldis.com
Air Filters
They are located at the return duct air inlets, at one or more central return air inlets, or at the air handler unit itself. Air filters remove dust and debris from building air.
Access ports to duct interior
Commercial ducts and some residential duct systems may have cleaning access ports. Residential HVAC ducts may have plugs indicating that the ducts were cleaned in the past.
Ductless air conditioning systems
These are also called “Split A/C systems”. A ductless air conditioning system may employ one or more wall-mounted cooling units.
Return air ducts
Return air ducts and registers to collect warm moist air from the occupied space and return it to the air handler unit. Also, some air conditioning installations do not provide return air registers and ducts in every room and use one or more “central air return inlets” instead.
Supply air ducts
Supply air ducts deliver cooled air to the occupied space. Also, they have the dual function of spreading out and directing the airflow into a location and permitting the regulation of airflow by opening or closing the register.
Supply air balancing dampers
Manual and motorized zone dampers may be installed inside the supply ducts at varying locations to permit balancing the airflow among different duct sections and thus among different building areas.
Thermostat(s)
Thermostats are used to turn the air conditioning on and off and to set the desired indoor temperature. Also, one thermostat will be located in each different air conditioning zone and will control an individual air handler unit’s operation.
A thermostat contains temperature sensors that govern the working of the heater and air conditioners. Also, the best place to install a thermostat remains near the center of the building. It should be away from damp and stuffy areas.
Moreover, some HVAC systems have more than one thermostat. Each thermostat controls a specific area. Therefore, the thermostat offers an energy-efficient way as the occupied areas can choose the temperature most convenient for the occupants.

Image Source: apexairco.com
Energy-efficient HVAC Systems
The HVAC systems account for approximately 40% of the total power consumption of a building. Thus, HVAC systems should optimize the available energy.
Energy Management Systems (EMS) or Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS) monitor and manage HVAC systems. This software sends notifications when the HVAC system is not working efficiently.
These systems give intelligent reports on identifying problem areas and provide recommendations for solving those problems.
They also integrate control systems to automate responses. Also, heating and cooling systems are automatically adjusted according to the temperature outside. So, constant monitoring ensures that neither overcooling nor overheating takes place.
Brands like Mitsubishi and Bryant provide energy-efficient HVAC systems.
Conclusion
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) Systems are instrumental in building design. Architectural design and HVAC installations go hand-in-hand. Therefore, make the HVAC installation plans at an early stage.
An HVAC system combines the processes of heating, cooling, and air ventilation using a thermostat and other devices. Thus, doing so enables the proper circulation of air inside the building. It also helps in modifying the building temperature according to the needs of the climate or season.
Also, there are various types of HVAC systems for commercial buildings like the Split AC System, the VRV or VRF system, and, the CAV and VAV system. All types of HVAC systems fulfill specific requirements for different-sized buildings.
There are several components of HVAC systems. Also, from air handlers to heating units, evaporator coils, and thermostats to ducts, every component has an indispensable role to play.
Technological advancements have allowed HVAC systems to become “intelligent”. Software like EMS (Energy Management Systems) provides energy efficiency.
This software identifies problem areas and then provides automated responses to solve those problems.
Thus, the bottom line is that great attention to detail must be paid while choosing HVAC systems that perfectly suit residential or commercial buildings. This system provides a safe and healthy indoor environment for any space.
Best AC brand in India | Top 10 air conditioners with prices
The summers in India are getting unbearable every year. Now, all of us are at the mercy of air conditioners to keep us cool a